Using Event Store Cloud
Networking
Each major cloud provider implements the concept of a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). A VPC gives you as the cloud user an isolated private network, to which you attach cloud compute resources (virtual machines, container orchestrators, etc) or managed resources, like database servers. VPCs are always in private network address spaces and therefore not directly accessible from the outside of the VPC without additional configuration and infrastructure.
Managed EventStoreDB clusters and instances are not accessible via public internet. You have the following options to ensure connectivity between Event Store Cloud and your workloads.
Cloud network peering
Normally, organisations build internal practices in regard to VPCs isolation and access level. In particular, you would expect that some or all VPCs are available for direct access from local networks on-premises, for developers to be able to access cloud resources. Cloud providers let their customers to connect on-premises networks to VPCs using site-to-site VPN connections. In addition, cloud customers often set up virtual private gateways to allow point-to-site VPN connections for their remote users.
Event Store Cloud deploys EventStoreDB clusters on a project-level VPC (network). By peering that network with your own VPC at the same cloud provider, you get access to the EventStoreDB cluster provisioned and managed by Event Store Cloud. Normally, your Ops engineers would be able to configure the routing and allow connecting to EventStoreDB clusters in the cloud.
Currently, peering links have the following limitations:
- For one peering link you can only specify a single IP range. It means that if your own cloud network has multiple IP ranges, you can only peer one of those. Workloads, which use other IP ranges, won't be able to access managed ESDB instances.
- For Azure, peering links have the "Allow gateway transit" property disabled. As the peering link is created from Event Store Cloud side, you cannot change this property. It means that the workload must be connected to the peered VN to access the managed ESDB instance.
We are addressing the limitations listed above in the coming releases of Event Store Cloud.
TailScale
Another options to connect to the cloud cluster is to use a third-party VPN offering, which might be easier to use. One example would TailScale, which is a WireGuard® based mesh VPN. In addition to the basic functionality of connecting devices in a mesh network, TailGate also allows connecting a subnet to the private VPN. For that, you'd need to provision a VM in the cloud, which is connected to the network peered with Event Store Cloud network. Since that machine would be able to access the EventStoreDB cluster, by configuring the TailScale subnet routing you will also make the cluster accessible for all users of your TailScale network.
Check our Tailscale guide for detailed instructions.
Data migration
Currently, the only way to migrate data to the cloud cluster or instance is by using live migration. Live migration can only handle small to medium size databases.
Cluster connection
Event Store Cloud unconditionally provisions secure EventStoreDB clusters with both TLS for TCP and SSL for HTTP and gRPC enabled. This configuration cannot be changed.
Cloud clusters use SSL certificates signed by the trusted public certificate authority and therefore you won't need to do any additional work that is usually associated with self-signed certificates.
After you provision the cloud cluster, you can find connection details for the cluster in the Cloud console.
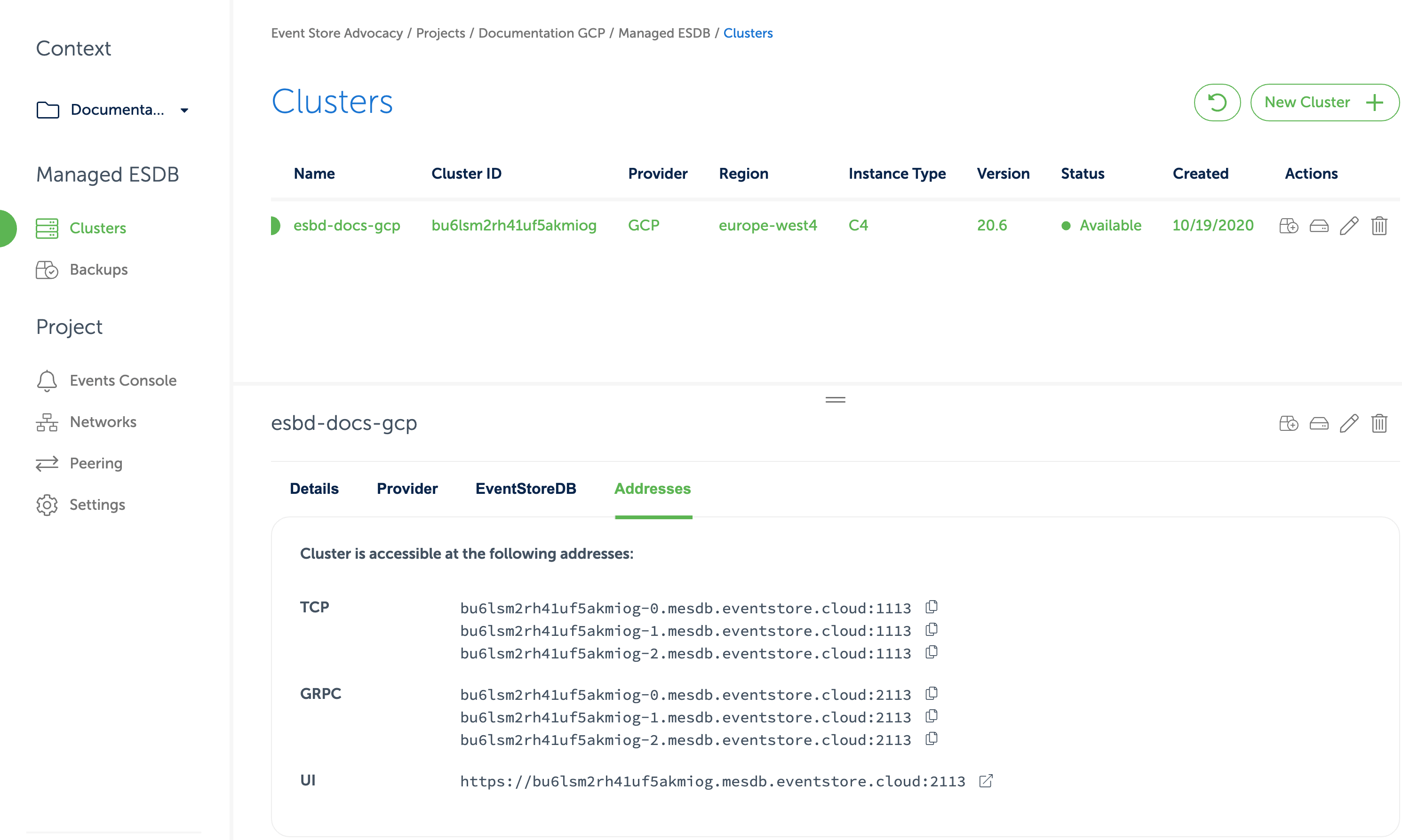
In the cluster details, you can find URIs for the EventStoreDB Admin UI and HTTP API, TCP client and gRPC client.
The DNS name of the cluster resolves to IP addresses of all the cluster nodes or to the IP address of a single instance, depending on the deployment topology.
Each cluster node has its own DNS name, which can be used for accessing individual nodes for node-specific operations like stats collection or scavenging.
Connect with Tailscale
In many organisations which work with the cloud, you can find the connection between the cloud networks and your local network already established using a Virtual Private Gateway or Site-to-Site VPN connection. However, if you're starting on the side and want to keep things simple, you can use Tailscale to connect to the Event Store Cloud cluster.
Follow the steps in this guide to connect to the Event Store Cloud cluster using Tailscale.